目录
使用数据库是开发基本应用的基础,借助于开发框架,我们已经不用编写原始的访问数据库的代码,也不用调用JDBC(Java Data Base Connectivity)或者连接池等诸如此类的被称作底层的代码,我们将从更高的层次上访问数据库,这在Springboot中更是如此,本章我们将详细介绍在Springboot中使用 Spring Data JPA 来实现对数据库的操作。
JPA是Java Persistence API的简称,中文名Java持久层API,是Sun官方提出的Java持久化规范,其设计目标主要是为了简化现有的持久化开发工作和整合ORM技术。JPA使用XML文件或注解(JDK 5.0或更高版本)来描述对象-关联表的映射关系,能够将运行期的实体对象持久化到数据库,它为Java开发人员提供了一种ORM工具来管理Java应用中的关系数据。 简单地说,JPA就是为POJO(Plain Ordinary Java Object)提供持久化的标准规范,即将Java的普通对象通过对象关系映射(Object-Relational Mapping,ORM)持久化到数据库中。由于JPA是在充分吸收了现有Hibernate,TopLink,JDO等ORM框架的基础上发展而来的,因而具有易于使用、伸缩性强等优点。
Spring Data JPA 是 Spring 基于 Spring Data 框架、在JPA 规范的基础上开发的一个框架,使用 Spring Data JPA 可以极大地简化JPA 的写法,可以在几乎不用写实现的情况下实现对数据库的访问和操作,除了CRUD外,还包括分页和排序等一些常用的功能。
以MySQL数据库为例,为了使用JPA和MySQL,首先在工程中引入它们的Maven依赖。
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.1.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>在Springboot核心配置文件 application.properties 中配置MySQL数据源和JPA。
######################################################## ### Spring datasource -- Datasource configuration. ######################################################## spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=UTF-8 spring.datasource.username = root spring.datasource.password = 123456 spring.datasource.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.type = org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource ######################################################## ### Java Persistence Api -- Spring jpa configuration. ######################################################## # Specify the DBMS spring.jpa.database = MYSQL # Show or not log for each sql query spring.jpa.show-sql = true # Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, update, validate, none) spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update # Naming strategy #[org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy #org.hibernate.cfg.DefaultNamingStrategy] spring.jpa.hibernate.naming-strategy = org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy # stripped before adding them to the entity manager) spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect其中,spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto 参数用来配置是否开启自动更新数据库表结构,可取create、create-drop、update、validate、none五个值。
- create 每次加载hibernate时,先删除已存在的数据库表结构再重新生成;
- create-drop 每次加载hibernate时,先删除已存在的数据库表结构再重新生成,并且当 sessionFactory关闭时自动删除生成的数据库表结构;
- update 只在第一次加载hibernate时自动生成数据库表结构,以后再次加载hibernate时根据model类自动更新表结构;
- validate 每次加载hibernate时,验证数据库表结构,只会和数据库中的表进行比较,不会创建新表,但是会插入新值。
- none 关闭自动更新
首先创建一些普通对象,用来与数据库的表建立映射关系,在此我们只定义了员工和部门两个实体来进行示例。
@Entity @Table(name = "tbl_employee") // 指定关联的数据库的表名 public class Employee implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; // 主键ID private String name; // 姓名 @ManyToOne @JoinColumn(name = "department_id") private Department department; // 部门 public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Department getDepartment() { return department; } public void setDepartment(Department department) { this.department = department; } }@Entity @Table(name = "tbl_department") public class Department implements Serializable{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; // 主键ID private String name; // 部门名称 public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }其中,注解@Entity用来标记该类是一个JPA实体类,并使用了注解@Table指定关联的数据库的表名;注解@Id用来定义记录的唯一标识,并结合注解@GeneratedValue将其设置为自动生成。
使用 JPA 进行数据持久化有两种实现方式。
- 方式一:使用Spring Data JPA 提供的接口默认实现,
- 方式二:自定义符合Spring Data JPA规则的查询方法,由框架将其自动解析为SQL。
使用Spring Data JPA接口(方式一)
Spring Data JPA提供了一些实现了基本的数据库操作的接口类,如下图所示。
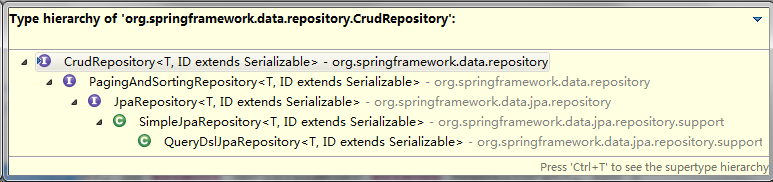
CrudRepository
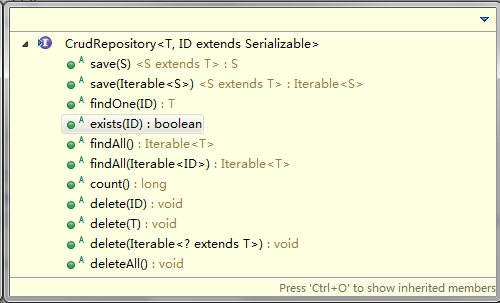
CrudRepository提供了一些简单的增删查改功能,接口定义如下。
package org.springframework.data.repository; import java.io.Serializable; @NoRepositoryBean public interface CrudRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends Repository<T, ID> { <S extends T> S save(S entity); // 保存并返回(修改后的)实体 <S extends T> Iterable<S> save(Iterable<S> entities); // 保存并返回(修改后的)实体集合 T findOne(ID id); // 根据ID获取实体 boolean exists(ID id); // 判断指定ID的实体是否存在 Iterable<T> findAll(); // 查询所有实体 Iterable<T> findAll(Iterable<ID> ids); // 根据ID集合查询实体 long count(); // 获取实体的数量 void delete(ID id); // 删除指定ID的实体 void delete(T entity); // 删除实体 void delete(Iterable<? extends T> entities); // 删除实体集合 void deleteAll(); // 删除所有实体 }PagingAndSortingRepository
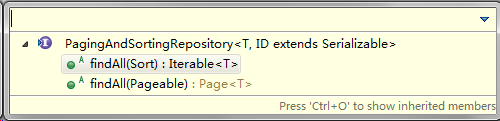
PagingAndSortingRepository继承于CrudRepository,除了具有CrudRepository接口的能力外,还新增了分页和排序的功能,接口定义如下。
package org.springframework.data.repository; import java.io.Serializable; import org.springframework.data.domain.Page; import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable; import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort; @NoRepositoryBean public interface PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends CrudRepository<T, ID> { Iterable<T> findAll(Sort sort); // 查询所有实体并排序 Page<T> findAll(Pageable pageable); // 分页查询实体 }JpaRepository
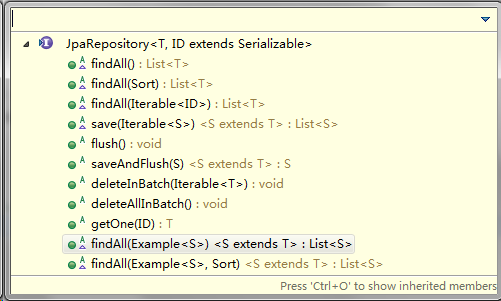
JpaRepository继承于PagingAndSortingRepository,所以它传递性地拥有了以上接口的所有方法,同时,它还继承了另外一个QueryByExampleExecutor接口,拥有了该接口匹配指定样例的能力,JpaRepository接口定义如下。
package org.springframework.data.jpa.repository; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.EntityManager; import org.springframework.data.domain.Example; import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort; import org.springframework.data.repository.NoRepositoryBean; import org.springframework.data.repository.PagingAndSortingRepository; import org.springframework.data.repository.query.QueryByExampleExecutor; @NoRepositoryBean public interface JpaRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID>, QueryByExampleExecutor<T> { List<T> findAll(); // 查询所有实体 List<T> findAll(Sort sort); // 查询所有实体并排序 List<T> findAll(Iterable<ID> ids); // 根据ID集合查询实体 <S extends T> List<S> save(Iterable<S> entities); // 保存并返回(修改后的)实体集合 void flush(); // 提交事务 <S extends T> S saveAndFlush(S entity); // 保存实体并立即提交事务 void deleteInBatch(Iterable<T> entities); // 批量删除实体集合 void deleteAllInBatch();// 批量删除所有实体 T getOne(ID id); // 根据ID查询实体 @Override <S extends T> List<S> findAll(Example<S> example); // 查询与指定Example匹配的所有实体 @Override <S extends T> List<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Sort sort);// 查询与指定Example匹配的所有实体并排序 }QueryByExampleExecutor
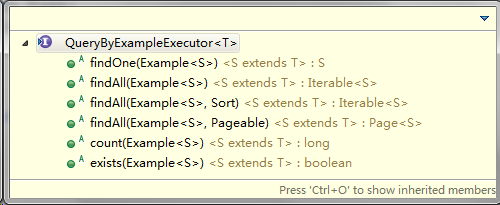
QueryByExampleExecutor接口允许开发者根据给定的样例执行查询操作,接口定义如下。
package org.springframework.data.repository.query; import org.springframework.data.domain.Example; import org.springframework.data.domain.Page; import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable; import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort; public interface QueryByExampleExecutor<T> { <S extends T> S findOne(Example<S> example); // 查询与指定Example匹配的唯一实体 <S extends T> Iterable<S> findAll(Example<S> example); // 查询与指定Example匹配的所有实体 <S extends T> Iterable<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Sort sort); // 查询与指定Example匹配的所有实体并排序 <S extends T> Page<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Pageable pageable);// 分页查询与指定Example匹配的所有实体 <S extends T> long count(Example<S> example); // 查询与指定Example匹配的实体数量 <S extends T> boolean exists(Example<S> example); // 判断与指定Example匹配的实体是否存在 }以部门实体资源库接口DepartmentRepository为例,只需继承CrudRepository接口便会自动拥有基础的增删查改功能,无须编写一条SQL。
@Repository public interface DepartmentRepository extends CrudRepository<Department, Long> { }自定义查询方法(方式二)
除了可以直接使用Spring Data JPA接口提供的基础功能外,Spring Data JPA还允许开发者自定义查询方法,对于符合以下命名规则的方法,Spring Data JPA能够根据其方法名为其自动生成SQL,除了使用示例中的 find 关键字,还支持的关键字有:query、get、read、count、delete等。
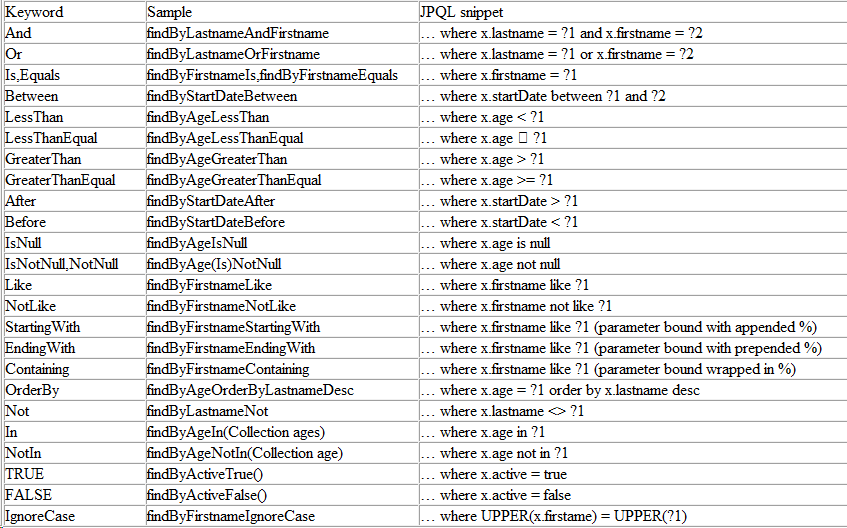
另外,Spring Data JPA 还提供了对分页查询、自定义SQL、查询指定N条记录、联表查询等功能的支持,以员工实体资源库接口EmployeeRepository为例,功能代码示意如下。
@Repository public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Long> { /** * 根据部门ID获取员工数量 */ int countByDepartmentId(Long departmentId); /** * 根据部门ID分页查询 */ Page<Employee> queryByDepartmentId(Long departmentId, Pageable pageable); /** * 根据员工ID升序查询前10条 */ List<Employee> readTop10ByOrderById(); /** * 根据员工姓名取第一条记录 */ Employee getFirstByName(String name, Sort sort); /** * 联表查询 */ @Query("select e.id as employeeId,e.name as employeeName,d.id as departmentId,d.name as departmentName from Employee e , Department d where e.id= ?1 and d.id= ?2") EmployeeDetail getEmployeeJoinDepartment(Long eid, Long did); /** * 修改指定ID员工的姓名 */ @Modifying @Transactional(timeout = 10) @Query("update Employee e set e.name = ?1 where e.id = ?2") int modifyEmployeeNameById(String name, Long id); /** * 删除指定ID的员工 */ @Transactional(timeout = 10) @Modifying @Query("delete from Employee where id = ?1") void deleteById(Long id); }为例验证上面接口的正确性,我们使用JUnit来进行测试,先增加一个JPA的配置类,代码如下。
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE) @Configuration @EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true) @EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = {"com.pengjunlee.repository"}) @EntityScan(basePackages = {"com.pengjunlee.entity"}) @EnableAutoConfiguration public class JpaConfiguration { @Bean PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor persistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor() { return new PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor(); } }其中,@EnableTransactionManagement注解用来启用JPA事务管理,@EnableJpaRepositories注解用来启用JPA资源库发现,@EntityScan注解用来启用实体发现。
配置类定义好之后,编写一个JUnit Test Case测试程序。
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes = JpaConfiguration.class) @TestPropertySource(locations = { "classpath:application.properties" }) public class JpaTest { @Autowired DepartmentRepository departmentRepository; @Autowired EmployeeRepository employeeRepository; @Test public void addDepartmentTest() { } @Test public void initData() { // 清空员工表中的数据 employeeRepository.deleteAll(); // 清空部门表中的数据 departmentRepository.deleteAll(); // 部门表中添加一个开发部 Department dept1 = new Department(); dept1.setName("开发部"); departmentRepository.save(dept1); // 部门表中添加一个测试部 Department dept2 = new Department(); dept2.setName("测试部"); departmentRepository.save(dept2); String[] names = new String[] { "lucy", "tom", "hanmeime", "jacky", "francky", "lilly", "xiaoming", "smith", "walt", "sherry" }; // 员工表中增加10条记录 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Employee emp = new Employee(); emp.setName(names[i]); if (i < 5) { emp.setDepartment(dept1); } else { emp.setDepartment(dept2); } employeeRepository.save(emp); } } @Test public void testCountByDepartmentId() { int count = employeeRepository.countByDepartmentId(19L); System.out.println(count); } @Test public void testQueryByDepartmentId() { Pageable pageable = new PageRequest(0, 10, new Sort(Sort.Direction.ASC, "name")); Page<Employee> emps = employeeRepository.queryByDepartmentId(19L, pageable); for (Employee emp : emps.getContent()) { System.out.println("员工姓名:" + emp.getName() + ",所属部门:" + emp.getDepartment().getName()); } } @Test public void testReadTop10ByOrderById() { List<Employee> emps = employeeRepository.readTop10ByOrderById(); for (Employee emp : emps) { System.out.println("员工姓名:" + emp.getName() + ",所属部门:" + emp.getDepartment().getName()); } } @Test public void testGetFirstByName() { Employee emp = employeeRepository.getFirstByName("xiaoming", new Sort(Direction.ASC, "id")); System.out.println("员工姓名:" + emp.getName() + ",所属部门:" + emp.getDepartment().getName()); } @Test public void testGetEmployeeJoinDepartment() { EmployeeDetail empDetail = employeeRepository.getEmployeeJoinDepartment(5L, 19L); System.out.println("员工姓名:" + empDetail.getEmployeeName() + ",部门名称:" + empDetail.getDepartmentName()); } @Test public void testModifyEmployeeNameById() { employeeRepository.modifyEmployeeNameById("chris", 5L); } @Test public void testDeleteById() { employeeRepository.deleteById(11L); } }热门文章
- 怀孕了让猫挠了轻微出血有事吗要***吗(怀孕让猫挠了怎么办)
- 2月6日|最高速度18.4M/S,2025最新Hysteria2免费节点高速订阅链接,便宜机场推荐
- 12月4日|最高速度22.9M/S,2024最新Hysteria2免费节点高速订阅链接,便宜机场推荐
- 宠物医院好评怎么写简短 宠物医院好评怎么写简短一点
- 新手养猫入门必备攻略图片(新手养猫应该准备些什么)
- 1月13日|最高速度22.8M/S,2025最新Hysteria2免费节点高速订阅链接,便宜机场推荐
- 兽药疫苗冷藏室温度(兽用疫苗冷藏温度)
- 1月24日|最高速度19.9M/S,2025最新Hysteria2免费节点高速订阅链接,便宜机场推荐
- 动物疫苗的作用是什么呢英文翻译(动物疫苗的作用是什么呢英文翻译成中文)
- 2月3日|最高速度21.3M/S,2025最新Hysteria2免费节点高速订阅链接,便宜机场推荐